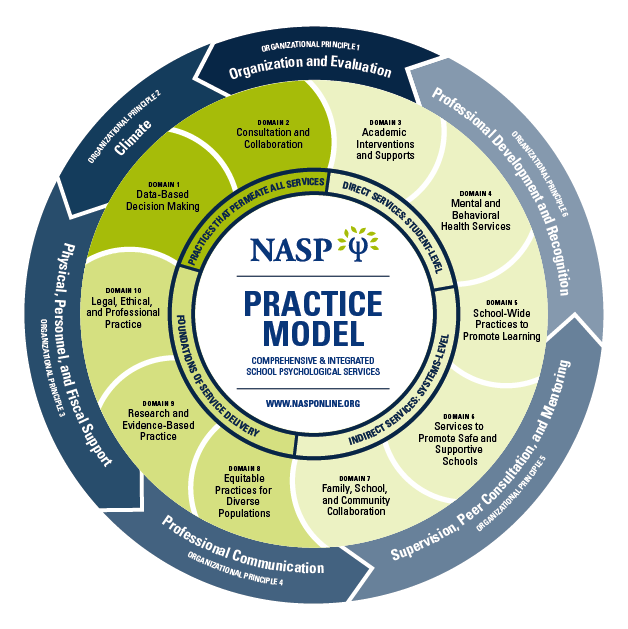
NASP Domains of Practice
PRACTICES THAT PERMEATE ALL ASPECTS OF SERVICE DELIVERYDomain 1: Data-Based Decision Making and Accountability-School psychologists have knowledge of varied models and methods of assessment and data collection for identifying strengths and needs, developing effective services and programs, and measuring progress and outcomes. As part of a systematic and comprehensive process of effective decision making and problem solving that permeates all aspects of service delivery, school psychologists demonstrate skills to use psychological and educational assessment, data collection strategies, and technology resources and apply results to design, implement, and evaluate direct interventions, psychological services, and programs. Examples of professional practices include:
Domain 2: Consultation and Collaboration-School psychologists have knowledge of varied models and strategies of consultation, collaboration, and communication applicable to individuals, families, schools and systems, and methods to promote effective implementation of services. As part of a systematic and comprehensive process of effective decision making and problem solving that permeates all aspects of service delivery, school psychologists demonstrate skills to consult, collaborate, and communicate effectively with others. Examples of professional practices include:
Direct and Indirect Services for Children, Families, and Schools: Student Level ServicesDomain 3: Interventions and Instructional Support to Develop Academic Skills-School psychologists have knowledge of biological, cultural, and social influences on academic skills; human learning, cognitive, and developmental processes; and evidence-based curricula and instructional strategies. School psychologists, in collaboration with others, demonstrate skills to use assessment and data collection methods and to implement and evaluate services that support cognitive and academic skills. Examples of professional practices include:
Domain 4: Interventions and Mental Health Services to Develop Social and Life Skills-School psychologists have knowledge of biological, cultural, developmental, and social influences on behavior and mental health, behavioral and emotional impacts on learning and life skills, and evidence-based strategies to promote social–emotional functioning, and mental and behavioral health. School psychologists, in collaboration with others, demonstrate skills to use assessment and data collection methods and to implement and evaluate services that support socialization, learning, and mental and behavioral health. Examples of professional practices include:
Systems-Level ServicesDomain 5: School-Wide Practices to Promote Learning-School psychologists have knowledge of school and systems structure, organization, and theory; general and special education; technology resources; and evidence-based school practices that promote learning and mental and behavioral health. School psychologists, in collaboration with others, demonstrate skills to develop and implement practices and strategies to create and maintain effective and supportive learning environments for children and others. Examples of professional practices include:
Domain 6: Preventive and Responsive Services-School psychologists have knowledge of principles and research related to resilience and risk factors in learning and mental health, services in schools and communities to support multitiered prevention, and evidence-based strategies for effective crisis response. School psychologists, in collaboration with others, demonstrate skills to promote services that enhance learning, mental and behavioral health, safety, and physical well-being through protective and adaptive factors and to implement effective crisis preparation, response, and recovery. Examples of professional practices include:
Domain 7: Family–School Collaboration Services-School psychologists have knowledge of principles and research related to family systems, strengths, needs, and culture; evidence-based strategies to support family influences on children’s learning and mental and behavioral health; and strategies to develop collaboration between families and schools. School psychologists, in collaboration with others, demonstrate skills to design, implement, and evaluate services that respond to culture and context and facilitate family and school partnerships and interactions with community agencies for enhancement of academic and social–behavioral outcomes for children. Examples of professional practices include:
Foundations of School Psychological Service DeliveryDomain 8: Diversity in Development and Learning-School psychologists have knowledge of individual differences, abilities, disabilities, and other diverse student characteristics; principles and research related to diversity factors for children, families, and schools, including factors related to culture, context, and individual and role difference; and evidence-based strategies to enhance services and address potential influences related to diversity. School psychologists provide professional services that promote effective functioning for individuals, families, and schools with diverse characteristics, cultures, and backgrounds and across multiple contexts. Understanding and respect for diversity in development and learning, and advocacy for social justice, are foundations for all aspects of service delivery. Examples of professional practices include:
Domain 9: Research and Program Evaluation-School psychologists have knowledge of research design, statistics, measurement, varied data collection and analysis techniques, and program evaluation sufficient for understanding research and interpreting data in applied settings. School psychologists demonstrate skills to evaluate and apply research as a foundation for service delivery and, in collaboration with others, use various techniques and technology resources for data collection, measurement, and analysis to support effective practices at the individual, group, and/or systems levels. Examples of professional practices include:
Domain 10: Legal, Ethical, and Professional Practice-School psychologists have knowledge of the history and foundations of school psychology; multiple service models and methods; ethical, legal, and professional standards; and other factors related to professional identity and effective practice as school psychologists. School psychologists demonstrate skills to provide services consistent with ethical, legal, and professional standards; engage in responsive ethical and professional decision-making; collaborate with other professionals; and apply professional work characteristics needed for effective practice as school psychologists, including respect for human diversity and social justice, communication skills, effective interpersonal skills, responsibility, adaptability, initiative, dependability, and technology skills. Examples of professional practices include:
|